When it comes to building walls, there are many different types to choose from. Two common types are retaining walls and boundary walls.
While the two may look similar, they serve different purposes and have different legal requirements. Understanding the differences between retaining walls and boundary walls can help you make informed decisions when it comes to building or maintaining walls on your property.
Understanding Retaining Walls
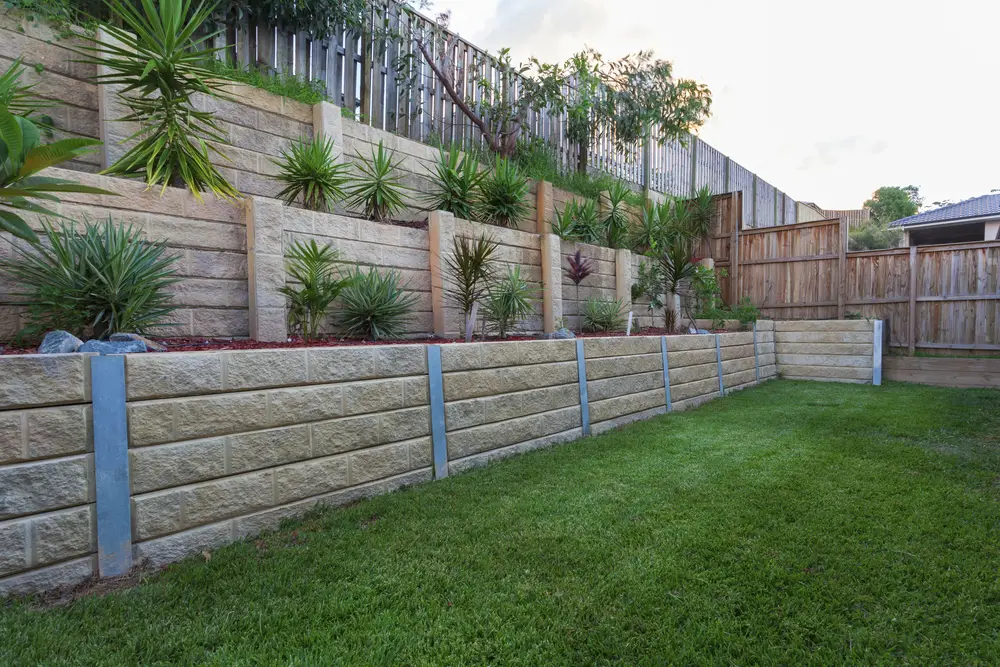

Retaining walls are structures built to hold soil in place and prevent it from sliding or eroding. They are also used to create functional slopes in landscaping and improve drainage.
In this section, we will discuss the structure and design, materials used, construction and support, and the role of retaining walls in landscaping.
1. Structure and Design
Retaining walls are designed to withstand the pressure of the soil they are holding back. The structure of a retaining wall is typically composed of a wall, footing, and backfill material.
The wall can be made of various materials such as concrete, brick, or stone. The footing is a horizontal base that supports the weight of the wall and distributes it evenly to the ground.
The backfill material is the soil or other material that is placed behind the wall to provide additional support.
The design of a retaining wall depends on various factors such as the height of the wall, soil type, and slope angle.
The wall can be designed with a sloping face or a vertical face. A sloping face helps to distribute the pressure of the soil more evenly, while a vertical face is more suitable for areas with limited space.
2. Materials Used
Retaining walls can be made of various materials such as concrete, brick, stone, or timber.
Concrete is the most commonly used material due to its strength and durability.
Brick and stone walls are also popular for their aesthetic appeal. Timber walls are less common but can be used in areas with limited space or where a more natural look is desired.
The choice of material depends on various factors such as the desired aesthetic, budget, and the environment. For example, timber walls are not suitable for areas with high moisture content or where termites are common.
3. Construction and Support
The construction of a retaining wall involves several steps such as excavation, wall construction, and backfilling.
The wall is constructed on top of the footing, and the backfill material is placed behind the wall to provide additional support. The backfill material is typically compacted in layers to ensure stability.
The support of a retaining wall can come from various sources such as soil reinforcement, tiebacks, or anchoring. Soil reinforcement involves adding steel or synthetic materials to the soil to increase its strength.
Tiebacks are cables that are anchored to the wall and extend into the soil to provide additional support. Anchoring involves drilling holes into the ground and inserting anchors to provide additional support.
4. Role in Landscaping
Retaining walls are an essential element in landscaping as they help to create functional slopes and prevent erosion.
They can also be used to create terraced gardens, raised flower beds, or seating areas. The design of the wall can be customized to match the desired aesthetic and complement the surrounding environment.
Understanding Boundary Walls
1. Definition and Use
A boundary wall is a structure that separates two pieces of land. It is typically built along the property line to define the boundary of a property.
The primary purpose of a boundary wall is to provide privacy and security to the property.
It also serves as a barrier to prevent trespassing and encroachment. Boundary walls can be made of a variety of materials, including brick, concrete, wood, and stone.
2. Construction Materials
Boundary walls can be constructed using a variety of materials, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common materials used for boundary walls are brick and concrete.
Brick walls are durable and attractive, but they can be expensive to build. Concrete walls are less expensive and can be constructed quickly, but they are not as attractive as brick walls.
Responsibility and Guidelines
The responsibility for maintaining a boundary wall falls on the property owner whose land the wall is located on.
However, if the wall is shared between two properties, both owners are responsible for maintaining it.
It is important to follow guidelines and regulations when building a boundary wall. In some areas, there are specific height restrictions and setback requirements that must be followed.
It is also important to ensure that the wall is built on the correct property line to avoid disputes with neighbors.
Here’s a table summarizing some common materials used in constructing boundary walls:
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Brick | Durable, attractive | Expensive |
| Concrete | Inexpensive, quick to construct | Not as attractive as brick |
| Wood | Natural look, easy to work with | Not as durable as brick or concrete |
| Stone | Attractive, durable | Expensive, requires skilled labor |
Comparing Retaining and Boundary Walls
1. Foundation and Footing
Retaining walls and boundary walls both require a strong foundation and footing to ensure stability.
However, retaining walls typically require a deeper foundation and wider footing due to the added weight and pressure of the soil they are retaining.
Boundary walls, on the other hand, can have a shallower foundation and narrower footing since they do not need to withstand the same amount of pressure.
2. Strength and Durability
Retaining walls are designed to withstand the lateral pressure of soil and water, making them stronger and more durable than boundary walls.
They are typically made of concrete, stone, or brick and can last for decades with proper maintenance.
Boundary walls, on the other hand, are not designed to withstand lateral pressure and are therefore less strong and durable. They are usually made of less sturdy materials like wood or vinyl and may need to be replaced more frequently.
3. Design Elements
Retaining walls and boundary walls also differ in their design elements.
Retaining walls are typically designed to blend in with the surrounding landscape and may feature decorative elements like plants or water features.
Boundary walls, on the other hand, are often designed to provide privacy and security and may feature gates or fences.
To summarize, retaining walls and boundary walls differ in their foundation and footing, strength and durability, and design elements.
Retaining walls require a deeper foundation and wider footing, are stronger and more durable, and are designed to blend in with the surrounding landscape.
Boundary walls, on the other hand, have a shallower foundation and narrower footing, are less strong and durable, and are designed to provide privacy and security.
Dealing with FOUR Common Property Issues
When it comes to common property issues, it’s essential to understand the difference between a retaining wall and a boundary wall.
A retaining wall is designed to hold soil in place, while a boundary wall is built to mark the boundary between two properties.
However, issues can arise when these walls are not maintained correctly, leading to disputes between neighbors. In this section, we’ll discuss how to deal with common property issues.
1. Encroachment
Encroachment occurs when a neighbor’s property extends beyond the boundary line and onto your property.
This can happen when a retaining wall or boundary wall is not built in the correct location. If you suspect that your neighbor’s property is encroaching on your land, you should first check your property’s boundary lines.
If you determine that your neighbor’s property is encroaching on your land, you should contact them and try to resolve the issue amicably.
2. Boundary Line Disputes
Boundary line disputes can arise when there is a disagreement about the location of the boundary line between two properties.
This can happen when a retaining wall or boundary wall is not built in the correct location or when there is confusion about the property’s boundary lines.
If you have a boundary line dispute with your neighbor, you should first check your property’s boundary lines and review any relevant documentation, such as property surveys or title deeds.
If you cannot resolve the dispute with your neighbor, you may need to seek legal advice.
3. Damage
Damage to a retaining wall or boundary wall can occur due to natural causes, such as erosion, or human causes, such as accidental damage or vandalism.
If your neighbor’s actions have caused damage to your retaining wall or boundary wall, you should contact them and try to resolve the issue amicably. If the damage is extensive, you may need to seek legal advice.
4. Replacement
If a retaining wall or boundary wall needs to be replaced, it’s essential to ensure that it is built in the correct location and to the correct specifications.
You should consult a professional contractor to ensure that the wall is built correctly.
If the wall is a common property, you should also consult with your homeowners’ association or strata management company to ensure that the wall is replaced in accordance with the relevant bylaws and regulations.
Understanding Insurance for Walls
When it comes to retaining walls and boundary walls, it’s important to understand how insurance works. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Insurers and Premiums
Different insurers may have different policies when it comes to covering walls.
It’s important to research and compare different insurance providers to find the best coverage for your needs.
Keep in mind that premiums may vary depending on the type of wall, its location, and other factors.
2. Covering Perils
In general, insurance policies will cover damage to walls caused by “perils,” or unexpected events that are beyond your control.
These may include natural disasters like floods or earthquakes, as well as accidents like a car crashing into the wall.
However, it’s important to read your policy carefully to understand exactly what is covered and what is not.
3. Replacement and Repair
If your wall is damaged and needs to be replaced or repaired, insurance may cover the cost.
However, keep in mind that there may be limits to how much coverage you can receive, and you may be responsible for paying a deductible before insurance kicks in.
Additionally, insurance may only cover the cost of repairing the wall to its original condition, rather than covering any upgrades or improvements you may want to make.
Keep in mind that insurance policies may vary, and it’s important to read your policy carefully to understand exactly what is covered and what is not. If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact your insurance provider for more information.
Conclusion
Overall, understanding the difference between a retaining wall and a boundary wall is crucial if you are planning to build a wall on your property. By choosing the right type of wall for your needs and ensuring that it is constructed correctly, you can enjoy the benefits of a sturdy and reliable structure for years to come.
